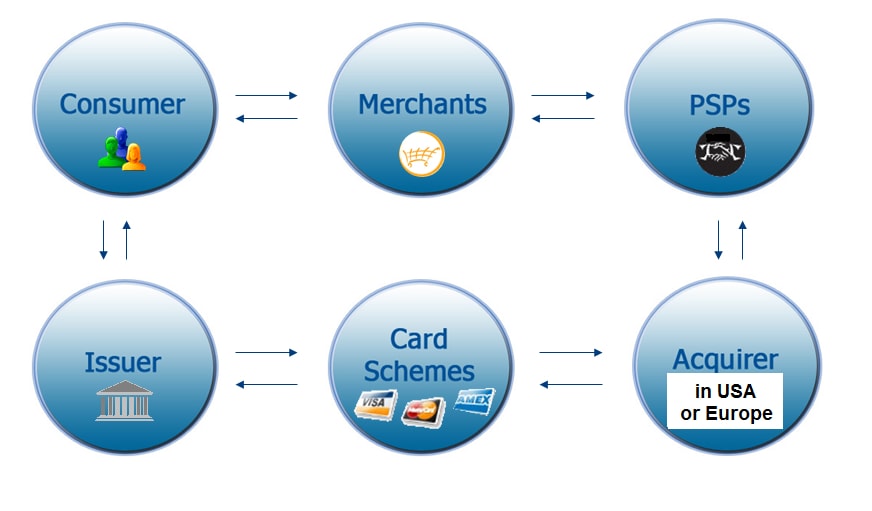
The players in the chain of payment
E-‐commerce and / or MOTO Merchant
An entity that sells remote goods / services to the cardholder and expects payment in return.
Payment Service Provider (PSP)
Technical interface that allows the merchant to offer its customers various payment methods – including payment by credit card and online payments. It is connected to the technical platform of the acquirer to pass on the data entered by the cardholder. Commonly called “Payment Gateway”.
Acquirer
Financial Institution approved by the “Card Associations”. Technically connected to the PSP via its platform. Manages, on behalf of the merchant, the payment process: authorization, data exchange and movement of funds to pay for the various players in the chain.
Card Associations
Visa and MasterCard networks. They authorize the transfer of funds to the
appropriate issuers using the data received from the platforms.
Issuer
Financial institutions that issue credit cards. They are responsible for approving or denying the transactions. The acquirer pays for all authorized transactions made by the cardholder and sends an invoice / statement to the cardholder.
Interchange
What is the Interchange?
This is an interbank percentage charged to merchants so they can accept credit cards. It is paid by the acquiring bank for the merchant to the issuing bank. It is used to offset some of the risks and costs that the issuing banks have by maintaining cardholder accounts.
Interchange rates are set by the credit card associations (Visa, MasterCard, Discover), and are by far the largest component of costs associated with the acceptance of credit cards (80% to 90% of total fees).
Who sets the Interchange Rates?
Visa and MasterCard set the rates and qualification requirements for each category of Interchange. This price is updated twice a year. There are thousands of different interchange rates depending on the type of card, the merchant profile etc.., but Interchange rates are the same regardless of the processor.
The Interchange fee charts are published on the Visa and MasterCard websites.
What factors affect the cost?
Interchange rates have a complex pricing structure based on:
- The card brand (Visa’s rates are different from MasterCard’s)
- The type of card (debit / credit rewards, corporate, international, etc.).
- The industry type (retail, restaurants, wholesalers, supermarkets, E-‐Commerce, schools, gas stations, etc.).
- The average ticket (small tickets get a preferential per transaction cost)
- How the merchant processes the transaction (swipe, online, mobile, etc..).
- Transactions are surcharged when they do not meet the requirements of the Interchange
Disclaimer: This item Publishes Information provided as general information only and is not Intended to replace box by box Appropriate advice from advisors. Definitions used are not intended to supersede any Regulatory or legal definition.

